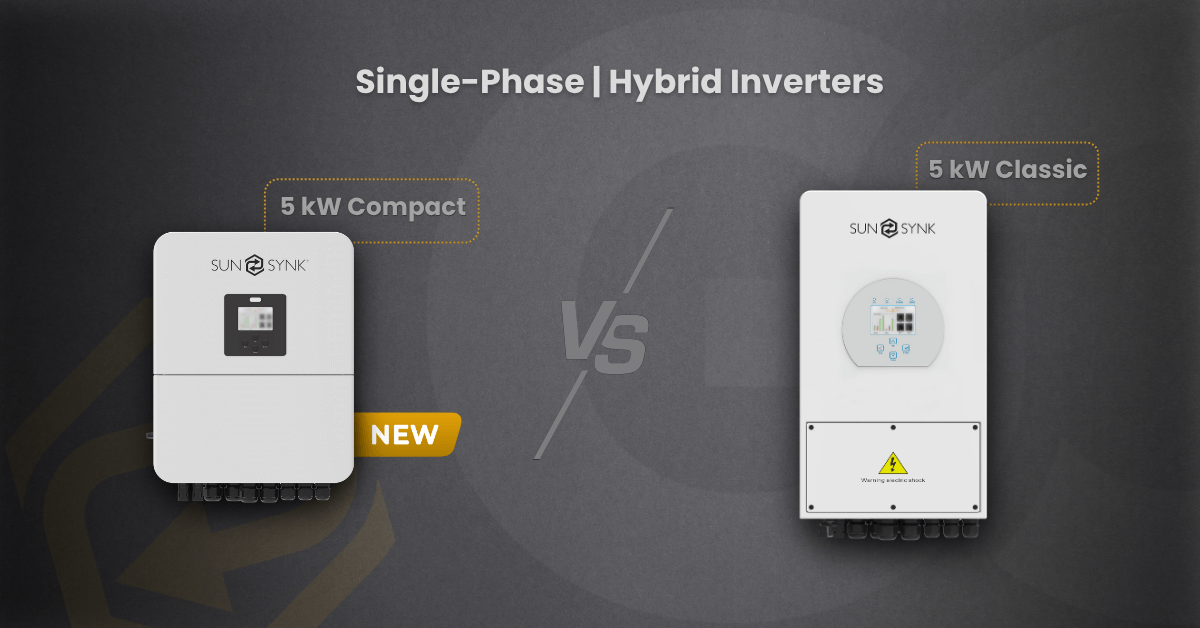
This report provides a detailed comparative analysis of two single-phase 5kW hybrid inverters from Sunsynk: the SYNK-5K-SG04LP1-SM2 (5kW Sunsynk Compact) and the SUNSYNK-5K-SG03LP1 (5kW Sunsynk Classic). While both models share the same core power rating and brand origin, they possess critical differences in their technical specifications that directly impact solar array design, installation suitability, and overall system performance. The purpose of this article is to provide an objective, data-driven comparison to guide informed technical purchasing and installation decisions for renewable energy professionals.
Core Performance and Efficiency
The inverter’s AC output and efficiency ratings are key to system performance and ROI, and both models show similar core metrics.
Table 2.1: Core AC Power and Efficiency Metrics
| Parameter | 5kW Compact | 5kW Classic |
| Rated AC Input/Output Active Power | 5000W | 5000W |
| Max. AC Input/Output Apparent Power | 5500VA | 5000VA |
| Peak Power (Off-Grid) | 2 times of rated power, 10 s | 2 times of rated power, 10 s |
| Max. Continuous AC Passthrough | 35A | 35A |
| Max. Efficiency | 97.60% | 97.60% |
| Euro Efficiency | 96.50% | 96.50% |
| MPPT Efficiency | >99% | >99% |
Analysis
Table 2.1 shows that both inverters deliver similar active power, peak off-grid capability, passthrough current, and efficiency. Under standard conditions, their energy conversion is equivalent.
The only minor difference is in the Maximum AC Apparent Power, where the 5kW Sunsynk Compact offers a slightly higher rating of 5500VA compared to the 5000VA of the 5kW Sunsynk Classic. This provides the 5kW Compact model with a marginal advantage in its ability to handle loads with lower power factors (reactive loads).
While their core performance is nearly identical, the primary and most significant differences between these models emerge in their capacity to interface with and manage solar energy input.
Decision Criteria: For systems with significant reactive loads (e.g., motors, pumps), the Compact offers a marginal advantage due to its higher apparent power rating.
PV String Input and Solar Generation Capability
The specifications governing photovoltaic (PV) input are a critical differentiator for any hybrid inverter. These parameters directly dictate the maximum size of the solar array that can be connected, which in turn defines the system’s total energy generation potential and its capacity for future expansion. It is in this domain that the two Sunsynk models differ significantly.
Table 3.1: PV Input Specifications
| Parameter | 5kW Compact | 5kW Classic |
| Max. PV Access Power | 10,000W | Not Listed |
| Max. PV/DC Input Power | 8000W | 6500W |
| Max. Operating PV Input Current | 18A + 18A | 13A + 13A |
| PV Input Voltage Range | 125V~500V | 370V (125V~500V) |
| MPPT Voltage Range | 150V~425V | 150V~425V |
| No. of MPPT / Strings per MPPT | 2 / 1+1 | 2 / 1+1 |
Analysis
The data reveals a substantial disparity in solar array capacity, positioning the Compact as the demonstrably superior model for maximising PV generation. Its maximum PV/DC input power of 8000W is 23% higher than the 6500W capacity of the Classic.
Critically, the Sunsynk Compact also specifies a “Max. PV Access Power” of 10,000W. This is a significant advantage, as it officially permits a higher DC/AC sizing ratio (oversizing the array), which enables greater energy harvesting in low-light conditions and minimises the impact of energy clipping during peak irradiance. Furthermore, its higher input current of 18A per MPPT (vs. 13A) ensures compatibility with modern, high-power solar modules. While both models feature dual MPPTs and a wide, flexible MPPT voltage range, the superior input specifications of the 5kW Compact make it the definitive choice for new installations aiming to maximise solar yield or for clients who wish to future-proof their system for later expansion.
Decision Criteria: The Compact is the unequivocal choice for installations seeking to maximise solar generation, employ high DC/AC sizing ratios, or accommodate future array expansion.
Battery System Integration and Charging
The battery input specifications are central to a hybrid inverter’s function, defining its compatibility with various energy storage technologies and its ability to manage the charging and discharging cycles of the battery bank. An effective battery interface is necessary for energy independence, load shifting, and backup power reliability.
Table 4.1: Battery Input and Charging Parameters
| Parameter | 5kW Compact | 5kW Classic |
| Battery Type | Lead-acid or Li-Ion | Lead-acid or Li-Ion |
| Battery Voltage Range | 40V~60V | 40V~60V |
| Max. Charging/Discharging Current | 120A | 120A (max.) |
| Charging Strategy for Li-Ion Battery | Self-adaption to BMS | Self-adaption to BMS |
| External Temperature Sensor | Not Listed | Yes |
Analysis
The core battery compatibility and performance metrics for both models are identical. They support the same battery types (Lead-Acid and Lithium-Ion), operate within the same 40-60V voltage range, and can deliver a powerful maximum charging and discharging current of 120A. Both also feature intelligent “Self-adaption to BMS” for seamless integration with modern lithium batteries.
The only specified difference is the inclusion of an External Temperature Sensor on the 5kW Classic. This feature, which is not listed in the datasheet for the 5kW Compact, allows the inverter to monitor the battery’s ambient temperature. This data can enable more precise, temperature-compensated charging, potentially enhancing the safety and longevity of the battery bank, particularly for lead-acid chemistries.
Decision Criteria: Where enhanced battery temperature monitoring and charging precision are prioritised, particularly for lead-acid batteries, the Classic holds a specific advantage.
Physical Design, Cooling, and Environmental Ratings
An inverter’s physical characteristics, cooling method, and environmental ratings are practical considerations that directly influence installation logistics, location planning, and long-term operational reliability. These factors determine where the unit can be safely installed and how it will withstand environmental conditions over its service life.
Table 5.1: Physical and Environmental Specifications
| Parameter | 5kW Compact | 5kW Classic |
| Cabinet Size (WxHxD) | 376 × 470 × 241.5 mm | 330 × 580 × 232 mm |
| Net Weight | 19 kg | 22.5 kg |
| Type of Cooling | Natural Cooling | Smart cooling |
| Ingress Protection (IP) Rating | IP65 | IP65 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40~60ºC, >45ºC Derating | -40~60ºC, >45ºC Derating |
Analysis
The physical designs present a clear trade-off. The Compact is significantly lighter at 19 kg (vs. 22.5 kg), making it easier for a single technician to handle and mount. However, it is also wider (376 mm vs. 330 mm). Conversely, the Classic is taller and heavier but has a narrower profile, which may be advantageous in installations with limited horizontal space.
A key operational difference lies in their cooling mechanisms. The 5kW Compact uses natural cooling, which implies a fanless design that operates silently and without moving parts that could fail. The 5kW Classic employs Smart cooling, which involves temperature-controlled fans. While this may provide more effective heat dissipation in extremely demanding environments, it introduces fans as a potential failure point and a source of operational noise. Reassuringly, both models share the same robust IP65 ingress protection rating, certifying them as dust-tight and protected against water jets, making them suitable for both indoor and protected outdoor installations.
Decision Criteria: The 5kW Compact is preferable for ease of handling and in noise-sensitive locations, while the 5kW Classic is the logical choice for installations with strict width limitations.
Key Differentiators for Decision-Making
While both the 5kW Compact and the Classic are capable single-phase hybrid inverters, the specific requirements and priorities of your solar installation project dictate the optimal choice. Core performance and efficiency are virtually identical, but critical differences in solar input capacity, physical design, and cooling technology will guide the final selection.
Below is a summary of the most critical differentiators to assist you in making a decisive choice.
- Solar Array Capacity: The Compact is superior for larger or future-proofed arrays due to its 8000W max input (vs. 6500W) and higher 18A string current (vs. 13A), accommodating modern high-power modules and enabling greater oversizing.
- Physical Footprint and Weight: The Compact is substantially lighter (19 kg), simplifying the mounting process. In contrast, the narrower profile of the Classic is better suited for installations with strict width constraints.
- Cooling Technology: The Compact features Natural Cooling for silent, maintenance-free operation. The Smart cooling of the Classic offers active heat dissipation but introduces fans as a potential source of noise and a future failure point.
- AC Power Headroom: The 5kW Compact has a slightly higher apparent power rating (5500VA vs. 5000VA), offering a minor technical advantage for sites with significant reactive loads.
Register with us or log in to the Get Off Grid portal for our broad range of Sunsynk Inverters. Available at all our branches | Get Off Grid Randburg | Get Off Grid Centurion | Get Off Grid Cape Town | Get Off Grid Zambia
Like this article? Please share!
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is intended for educational and informational purposes only. Every effort has been made to ensure accuracy. However, we advise that readers consult datasheets and installation manuals to verify information. For specific project requirements or additional guidance, please contact the Get Off Grid technical team.